Companies seeking to expand their remote workforce into Canada must adhere to the country's unique labor laws, which include providing mandatory employee benefits.
While global employers are required by law to contribute to Canada’s national healthcare and pension system, it is standard practice for employers to offer supplemental medical and retirement benefits. Offering comprehensive coverage and additional saving opportunities give companies a competitive advantage and help retain top talent.
Read this guide to understand mandatory and supplemental employee benefits in Canada and learn what you should offer to ensure compliance and keep your talent happy.
What benefits do Canadian employees get?
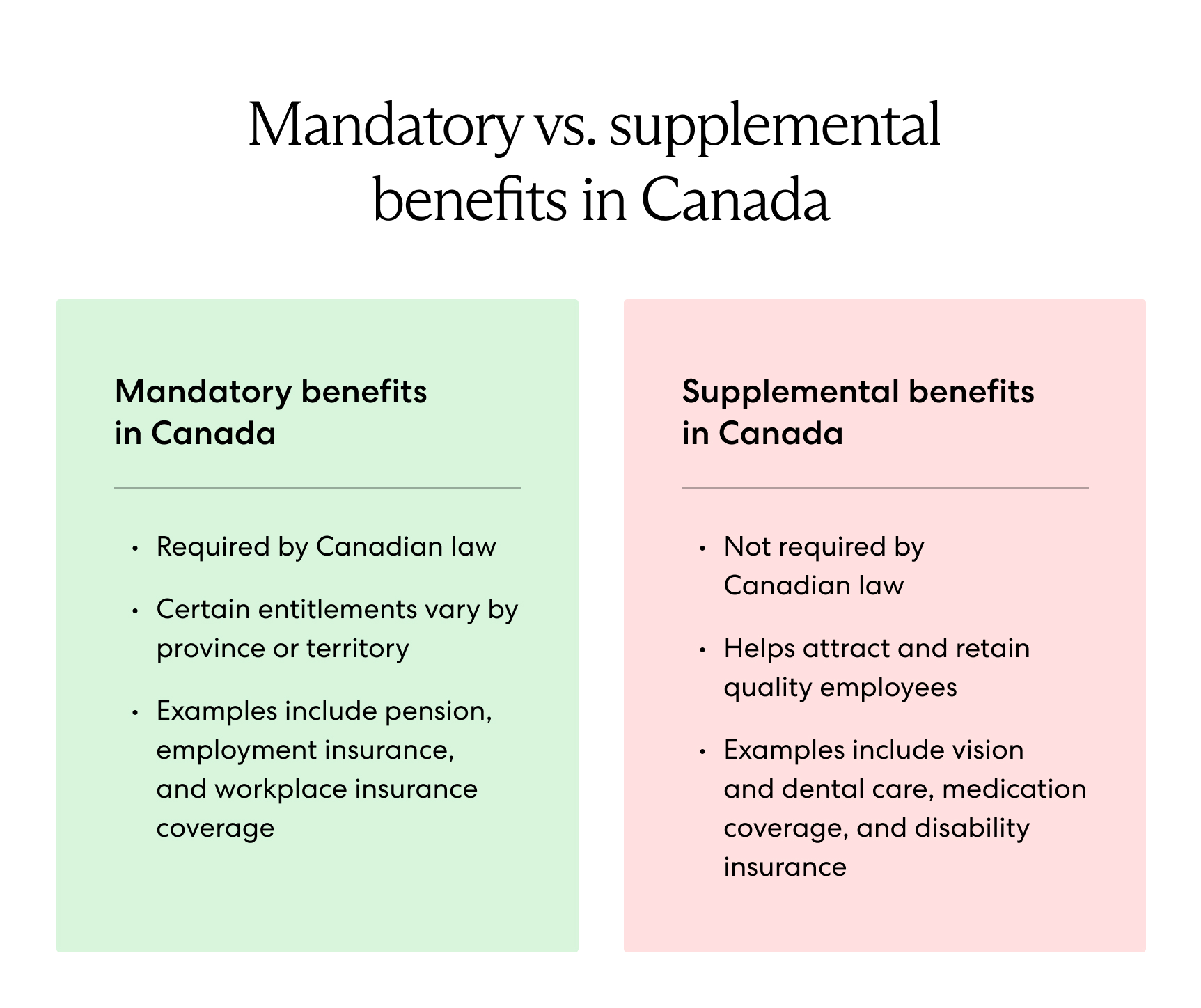
Mandatory benefits, also known as statutory benefits, are required by Canadian employment law. All Canadian citizens receive medical benefits as part of the national healthcare system. Statutory employee benefits in Canada include:
- Provincial healthcare coverage
- Pension contributions
- Employment insurance
- Survivor insurance
- Workers' compensation insurance
Read more about statutory benefits here.
Employers also offer supplemental benefits to ensure comprehensive coverage and employee satisfaction. Some common supplemental benefits in Canada include:
- Supplemental health insurance
- Group registered retirement savings
- Life coverage
- Long-term disability benefits
Mandatory benefits for employees in Canada
Canadian employees are entitled to certain mandatory benefits, and employers are responsible for meeting those requirements and making the correct contributions. Mandatory employee benefits in Canada include the following:
Provincial healthcare insurance
The public healthcare system in Canada guarantees that all Canadian residents have access to healthcare. Canadian Medicare provides these health benefits, and all employees are eligible for basic medical care and standard hospital care. Government tax revenue from Canada’s 13 provinces fund healthcare insurance. Healthcare coverage varies depending on the province or territory.
Pension: Canada Pension Plan and Quebec Pension Plan
The Canada Pension Plan covers employees who work outside of Quebec while the Quebec Pension Plan covers employees who work in Quebec. These plans are mandatory for all employers.
The Canada Pension Plan (CPP) is a taxable benefit that replaces part of an employee’s income when they retire. The employee and employer share monthly contributions. In 2023, the contribution rate is 5.95% for a maximum annual contribution of $3,754. The amount an employee receives upon retirement is based on their average earnings, CPP contributions, and age when they decide to start the retirement pension. A contributor must be at least 60 years old to qualify for CPP retirement pension.
The Québec Pension Plan (QPP) is a taxable public insurance plan that provides employees and their families with financial protection for retirement, death, or disability. Contributions are split equally between the employee and employer. The 2023 contribution rate is 12.8% and applies to earnings between $3,500 and $64,900. The amount of pension an employee receives is calculated based on the earnings recorded under their name since 1966 (the year the Quebec Pension Plan started) and the age when the contributor’s pension began. A contributor can receive their retirement pension as early as age 60.
Employment Insurance (EI)
Employment Insurance (EI) provides temporary income support to unemployed workers while they look for employment or take time off from work due to specific life events. EI covers illness, pregnancy, caring for a newborn, a newly adopted child, or a critically ill or injured person. Workers receive EI benefits only if they have paid premiums in the past year and meet certain entitlement conditions.
Survivor insurance
Survivor insurance in Canada is similar to life insurance, where the legal spouse or common-law partner of a deceased employee receives monthly payments. The CPP or QPP provides survivor insurance benefits, and all employees between 18 and 70 are eligible. The amount the survivor receives depends on their age at the time of the contributor’s death and their retirement pension.
Provincial workers’ compensation plans
All Canadian employees are eligible for workers’ compensation, which provides insurance for medical treatment and salary protection for employees who experience workplace injuries or illnesses. Workers’ compensation varies by province, and the benefits are dependent on the industry in which the employee works.
Learn more: Guide to Workers' Compensation in Canada
Common and supplemental employee benefits in Canada
In addition to statutory benefits, employees in Canada expect supplemental benefits. While it’s not required by law, offering supplemental benefits reduces your team’s financial burden and helps increase employee attraction and retention when seeing to hire employees in Canada. It also sets your company apart as an employer of choice in a competitive hiring market.
Learn more: What Are Supplemental Benefits?
Let’s look at common supplemental benefits Canadian employees value most.
Supplemental health insurance
Employers often offer supplemental health insurance plans that provide coverage beyond the basic medical and hospital care employees receive through the Canadian Medicare scheme. Private medical plans offer shorter waiting periods and provide better access to general healthcare treatment and specialty care. Additionally, private insurance plans provide coverage for services such as dental, vision, prescriptions, and various paramedical procedures.
Group registered retirement savings
It is common for employers to offer supplementary pension benefits and contribute a higher percentage to an employee’s retirement fund. Through Group Registered Retirement Savings Plans (GRRSP), employers match a tax-deductible percentage of the employee’s contributions.
However, risks are involved if an employee or employer contributes more than the deduction limit allows. If you exceed your GRRSP deduction limit by more than $2,000, you must pay a 1% tax on the excess contributions.
Life coverage and long-term disability benefits
Employers are recommended to offer life coverage and long-term disability benefits as part of their comprehensive benefits packages.
Life coverage insurance helps the survivors of a late employee handle the resulting financial impact of that employee’s passing. Receivers can use the benefit to replace income, provide for dependents, pay for funeral expenses, pay off debts, or make charitable donations.
Employers offer long-term disability (LTD) insurance to employees who become disabled or cannot work. The employer fully funds the LTD insurance and provides the employee a percentage of their income when they are ill, injured, or disabled for an extended period.
Read more about supplemental and robust global employee benefits here.
What is the average cost of employee benefits in Canada?

Statutory and supplementary benefits in Canada are additional costs to an employee’s gross salary. On average, Canadian employee benefits typically cost 15% of payroll for a smaller company and as much as 30% for a larger business.
Ultimately, the average cost you can expect to pay on benefits for your Canadian employees depends on the coverage level you choose to provide. An experienced partner, such as an employer of record (EOR) in Canada, that's knowledgeable in the country's national and provincial employment laws and regulations can help you determine a complete benefits package best suited for your workforce.
Learn more: Complete guide to Payroll Taxes in Canada
Care for your Canadian team with Velocity Global
Velocity Global simplifies your expansion into Canada. Our Global Benefits solution helps you attract and retain top talent with benefits and support that go above and beyond. Our team of dedicated experts can design comprehensive, market-specific packages that offer competitive benefits and maintain compliance with local statutory requirements.
Ensure your global team’s benefits are covered by contacting Velocity Global today.



